Examples:
1. An e-commerce company can use Cloud Data Fusion to ingest and transform data from various sources, such as transactional databases, user behavior logs, and third-party APIs, into a unified data warehouse for analytics and reporting.
2. A healthcare organization can leverage Cloud Data Fusion to clean, normalize, and enrich patient data from multiple systems to improve the accuracy of machine learning models for predicting patient outcomes.
Costs:
Cloud Data Fusion has a pay-as-you-go pricing model based on the type of instance (Basic or Enterprise) and the duration of instance usage. You are also billed for the Dataproc clusters used to execute your pipelines. Detailed pricing information can be found on the Cloud Data Fusion pricing page.
Pros:
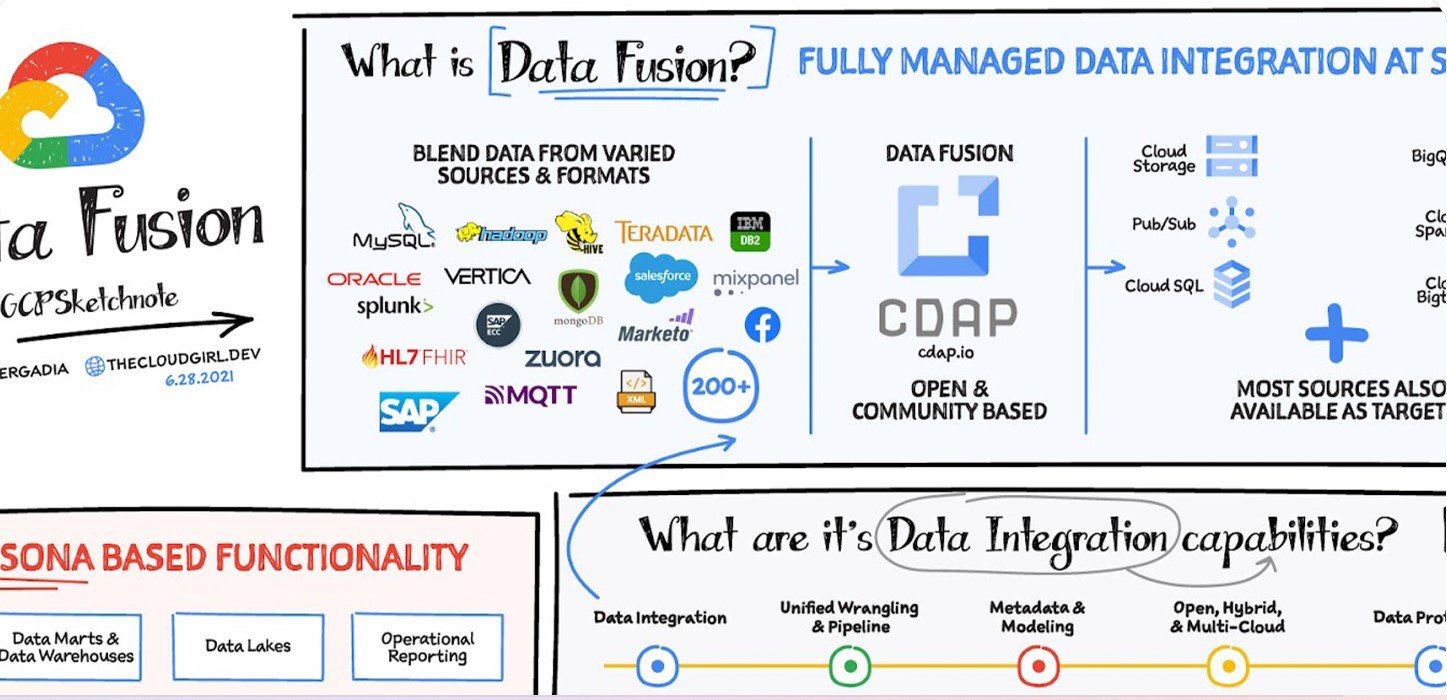
– Fully managed, cloud-native service simplifying data integration and transformation
– Visual interface for designing data pipelines, eliminating the need for manual coding
– Built on the open-source project CDAP, supporting a wide range of data sources and transformations
– Integrates with other GCP services such as Cloud Storage, BigQuery, and Dataproc
– Supports custom plugins for extending functionality
Cons:
– Limited control over the underlying infrastructure and performance tuning compared to self-managed solutions
– May require adapting existing data integration and transformation workflows to the Data Fusion paradigm
– Can be more expensive than custom solutions for large-scale or complex data processing tasks
Cloud Data Fusion in GCP is a powerful managed service for data integration and transformation tasks. Its visual interface, support for various data sources and transformations, and integration with other GCP services make it an attractive option for organizations looking to simplify their data processing workflows. By understanding the capabilities, costs, pros, and cons of Cloud Data Fusion, organizations can make informed decisions about implementing this data integration service in their GCP environment.